Servo Motor: Types, Working, Applications, and Complete Guide
A servo motor is a high-precision electromechanical device used for accurate control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. This complete guide covers its types, working principle, features, and applications across industries such as robotics, automation, and manufacturing. Learn how servo motors operate, their benefits, and how to choose the right model for your specific project or industrial needs.
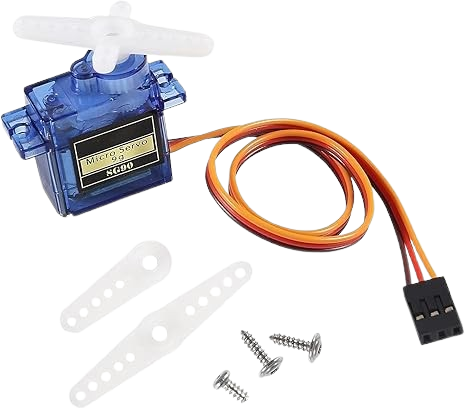

Device Overview
Introduction
A servo motor is a special type of motor designed for precise control of movement. It can control angular (rotational) or linear (straight) position, speed, and acceleration with high accuracy. Unlike normal motors that just spin continuously when power is applied, a servo motor moves to an exact position based on the control signal it receives.
These motors are widely used in automation, robotics, manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics because they provide excellent speed control, torque, and positioning accuracy. If you have ever seen a camera lens automatically focus, a robotic arm moving smoothly, or an automatic door opening at the right moment — there is a high chance a servo motor is doing the job.
What is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is basically an actuator that combines a motor, a control circuit, and a feedback system.
-
The motor provides the movement.
-
The control circuit decides how far and how fast the motor should move.
-
The feedback device (usually a sensor or encoder) constantly checks the motor’s position and sends that information back to the controller.
How Does a Servo Motor Work?
The working of a servo motor is based on a closed-loop control system:
-
Command Signal – A controller sends an electrical signal to the servo motor telling it the target position or speed.
-
Signal Processing – The motor’s internal circuit compares the desired position with the actual position from the feedback device.
-
Error Detection – If there’s a difference (called “error”), the motor adjusts itself to reduce that error.
-
Precise Movement – This process repeats continuously, so the motor always stays exactly where it needs to be.
Main Components of a Servo Motor
-
Motor (AC or DC) – Generates motion.
-
Control Circuit – Interprets input signals and controls motor operation.
-
Feedback Device – Monitors position and speed.
-
Gearbox – Adjusts speed and increases torque output.
-
Housing/Enclosure – Protects internal parts from dust and damage.
Types of Servo Motors
Servo motors come in different types based on power supply, motion type, and application.1. AC Servo Motor
- Runs on alternating current.
- Highly reliable, durable, and accurate.
- Used in heavy industrial machines and automation.
2. DC Servo Motor
- Runs on direct current.
- Simple to control and provides quick response.
- Common in hobby electronics, small robots, and consumer devices.
3. Positional Rotation Servo Motor
- Rotates within a fixed range (e.g., 0° to 180° or 0° to 270°).
- Perfect for controlling arms, flaps, and camera mounts.
4. Continuous Rotation Servo Motor
- Can spin continuously in both directions like a regular motor.
- Ideal for driving wheels or conveyor belts.
5. Linear Servo Motor
- Produces straight-line motion instead of rotation.
- Used in CNC machines, packaging equipment, and precision tools.
Advantages of Servo Motors
-
High Accuracy – Can position within fractions of a degree.
-
Fast Response – Adjusts speed and position quickly.
-
High Torque – Delivers good torque even at low speeds.
-
Energy Efficient – Consumes less power when idle.
-
Reliable Operation – Works well in continuous use.
Disadvantages of Servo Motors
- More expensive than standard motors.
- Requires a controller and proper wiring.
- Can overheat if overloaded.
- More complex to maintain than simple motors.
Applications of Servo Motors
Servo motors are used in a wide range of fields:-
Robotics – For arm movement and precise control.
-
CNC Machines – For accurate cutting and shaping.
-
Camera Systems – For lens focusing and gimbal stabilization.
-
Automatic Doors – For controlled opening and closing.
-
Antenna Positioning – For adjusting satellite dishes.
-
Medical Equipment – For precision movement in diagnostic machines.
-
Packaging Machines – For timed and accurate operations.
-
Printing Presses – For paper alignment and ink application.
How to Choose the Right Servo Motor
When selecting a servo motor, keep these factors in mind:-
Torque Requirement – How much rotational force you need.
-
Speed Requirement – How fast the motor needs to move.
-
Power Supply Type – AC or DC.
-
Environment – Will it face dust, heat, or moisture?
-
Size and Weight – Especially important for portable equipment.
-
Budget – Balance between cost and performance.
Real-Life Example: Servo Motor in a Camera Gimbal
A camera gimbal uses servo motors to keep the camera steady while filming. Here’s how it works:
-
Sensors in the gimbal detect movement or shaking.
-
Servo motors instantly adjust the camera’s position to cancel out the movement.
- The result is smooth, professional-quality video even when walking or moving quickly.
Why Servo Motors Are Perfect for This:
- High precision for angle adjustments.
- Quick reaction time to sensor input.
- Silent operation, which is ideal for filming.
Conclusion
Servo motors are one of the most versatile and precise motion control devices available today. They are used in industries, household devices, and even entertainment technology because of their ability to deliver accurate, fast, and controlled movement.
By understanding their types, working principles, benefits, and applications, you can select the right servo motor for your needs — whether it’s for industrial machinery, consumer electronics, or creative projects.
With their unmatched precision and efficiency, servo motors will continue to play a key role in the advancement of modern technology.Where to Buy
| Platform | Price | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
₹99 | Buy Now |
Prices may vary. Click on "Buy Now" to check current availability and pricing.
Administrator
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about Servo Motor: Types, Working, Applications, and Complete Guide. Find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
User Reviews & Comments
Share your experience with this IoT device. Your feedback helps our community make informed decisions!
Share Your Experience
Help others by sharing your thoughts about this IoT device.
Related Devices
Explore more IoT devices in the same category
Discover the ultimate guide to relay modules for IoT! Learn their features, applications, and setup tips for smart automation. From controlling appliances to building IoT projects, this blog covers types, specifications, and wiring techniques. Perfect for beginners and experts, unlock the power of relay modules to enhance your IoT solutions. Stay ahead in smart technology with our expert insights and practical advice.
Discover how DC motors power real-world IoT applications. This complete guide covers DC motor types, working principles, benefits, and step-by-step integration for smart devices. Learn how to use DC motors in IoT projects with precision and efficiency. Ideal for developers, students, and IoT engineers seeking reliable motor control solutions.
Discover how electromagnets are transforming IoT technology with smart functionality, precision control, and energy efficiency. This guide explains their working principle, real-world applications, and benefits in connected systems. Ideal for developers, tech enthusiasts, and IoT project creators seeking advanced automation solutions in 2025.
Discover everything about IoT buzzers, from how they work to their real-world applications in smart devices and automation systems. This guide explains the different types of buzzers, their features, advantages, and common use cases in industries, homes, and electronics projects.



No Reviews Yet
Be the first to share your experience with this IoT device!