What is a Photoresistor (LDR) in IoT? Working, Applications & Circuit Examples Explained
Discover how photoresistors (LDRs) work in IoT projects. Learn about their functions, real-world applications, circuit integration, and why they are essential in modern smart systems. This detailed guide helps electronics and IoT enthusiasts understand light sensors and their role in automation. Perfect for students, hobbyists, and developers looking to build smarter, light-based solutions.

Device Overview
Introduction
A photoresistor, also known as an LDR (Light Dependent Resistor), is a light-sensitive electronic component whose resistance changes based on the intensity of light falling on it. These components are widely used in various electronics, automation, and sensor-based systems to detect and respond to changes in ambient light.
How Does a Photoresistor Work?
A photoresistor works on the principle of photoconductivity — a phenomenon where the material becomes more conductive (lower resistance) when exposed to light.
-
In darkness, the resistance of the LDR is very high (in the mega-ohm range).
-
In bright light, the resistance drops significantly (to a few hundred ohms).
This unique behavior makes it an excellent choice for designing light detection and automation systems.
Construction of a Photoresistor
A typical photoresistor consists of:-
A semiconducting material such as cadmium sulfide (CdS).
- The material is arranged in a zig-zag pattern on an insulating base.
- Two metal leads are attached for connection in a circuit.
- The entire structure is enclosed in a transparent plastic case to allow light entry.
Types of Photoresistors
There are mainly two types of photoresistors based on their behavior and materials:
1. Intrinsic Photoresistors
- Made of pure semiconductor materials (e.g., pure silicon or germanium).
-
Sensitive to high-intensity light.
- Slower response time.
-
Used in scientific and research applications.
2. Extrinsic Photoresistors
- Made by doping semiconductor materials (e.g., CdS doped with copper).
-
Higher sensitivity to visible light.
- Faster and more stable response.
-
Widely used in consumer electronics and automation systems.
Characteristics of Photoresistors
| Property | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Resistance in Dark | High (up to 10 MΩ) |
| Resistance in Light | Low (few hundred Ω) |
| Response Time | 20ms to 50ms |
| Material | CdS, CdSe |
| Sensitivity Range | 400–700 nm (visible light) |
Advantages of Photoresistors
-
Cost-effective and readily available
-
Simple to use in circuits
-
Low power consumption
-
Ideal for ambient light detection
-
Non-polarized component (can be connected in any direction)
Disadvantages of Photoresistors
-
Slow response time (not ideal for fast-changing light)
-
Not suitable for precise light measurement
-
Affected by temperature
-
Toxic materials (CdS) – may not be RoHS compliant
Applications of Photoresistors
Photoresistors are used in various real-world applications such as:-
Street lights – automatic ON/OFF based on sunlight.
-
Solar garden lights
-
Camera light meters
-
Light-sensitive alarms
-
Brightness control in displays
-
Industrial automation systems
-
Security and motion detection systems
Practical Example: Photoresistor-Based Light Detection Circuit
Objective:
To automatically turn ON an LED when the light level drops below a certain threshold (i.e., it's dark).Components Needed:
- 1 × Photoresistor (LDR)
- 1 × 10kΩ resistor
- 1 × NPN transistor (e.g., BC547)
- 1 × LED
- 1 × Power supply (5V)
Circuit Description:
-
The LDR and 10kΩ resistor form a voltage divider circuit.
- The voltage at the divider's junction changes with light intensity.
-
This voltage is fed to the base of the transistor.
-
When it’s dark, voltage increases, turning ON the transistor, which in turn lights the LED.
Outcome:
-
Light ON → LED OFF
- Light OFF → LED ON
Where to Buy
| Platform | Price | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
₹60 | Buy Now |
Prices may vary. Click on "Buy Now" to check current availability and pricing.
Administrator
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about What is a Photoresistor (LDR) in IoT? Working, Applications & Circuit Examples Explained. Find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
User Reviews & Comments
Share your experience with this IoT device. Your feedback helps our community make informed decisions!
Share Your Experience
Help others by sharing your thoughts about this IoT device.
Related Devices
Explore more IoT devices in the same category
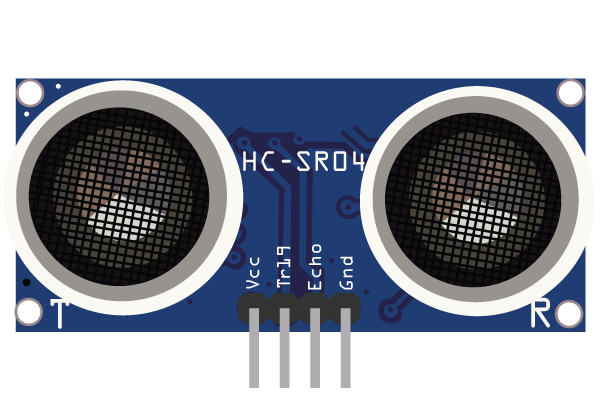
Discover how the Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04 works and how to use it in IoT projects. This detailed guide covers its working principle, pin configuration, interfacing with Arduino, applications in smart systems, and complete circuit setup. Ideal for beginners and IoT developers looking to integrate distance sensing in real-time projects.
A vibration sensor is a crucial device used to detect and measure vibrations in machines, structures, and environments. This complete guide covers how vibration sensors work, their different types, applications across industries, and factors to consider before selection. Learn how these sensors improve safety, enhance performance, and prevent costly equipment failures.
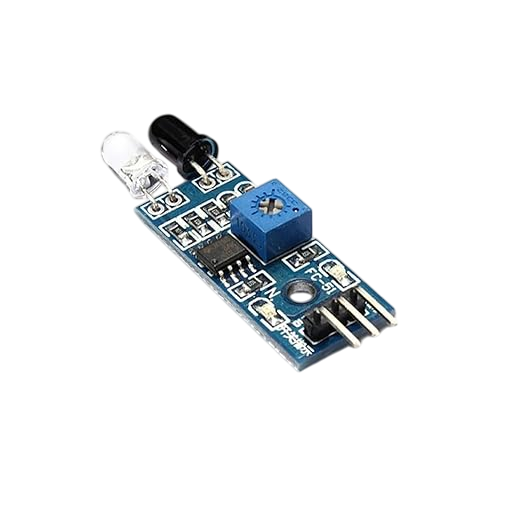
Discover everything about IR sensors used in modern IoT applications. Learn their types, working principles, interfacing methods, and real-world uses. This complete guide helps developers and engineers choose the best IR sensor for smart electronics and automation projects with reliable performance.
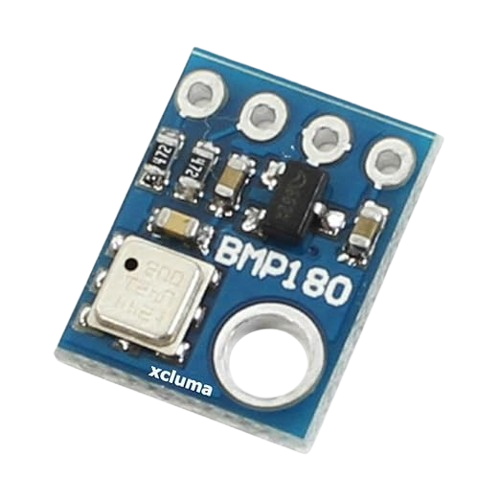
The BMP180 sensor is a high-precision digital barometric pressure sensor widely used for measuring atmospheric pressure and temperature. This detailed guide covers its key features, specifications, working principle, and practical applications. Learn how the BMP180 delivers accurate environmental data for various projects, along with benefits and usage tips to ensure reliable and efficient performance.
The Hall Effect Sensor is a key electronic component that detects magnetic fields and converts them into electrical signals. Widely used in IoT devices, robotics, and industrial systems, this sensor provides accurate, contactless, and reliable performance. In this blog, we explain how the Hall Effect Sensor works, its types, advantages, and real-world applications. From current measurement to speed detection, it plays a vital role in automation and smart technology.
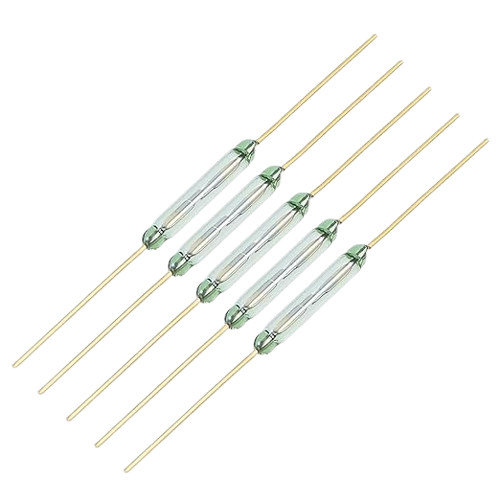
Reed Switch is a simple but powerful electronic component widely used in IoT devices and smart applications. This complete guide explains its working principle, different types, key advantages, and real-world applications. Whether you are an engineer, student, or IoT enthusiast, understanding Reed Switch technology helps in building efficient, reliable, and cost-effective projects with modern sensor solutions.



No Reviews Yet
Be the first to share your experience with this IoT device!