ESP8266 WiFi Module: Features, Specifications, Pinout, and Programming Guide
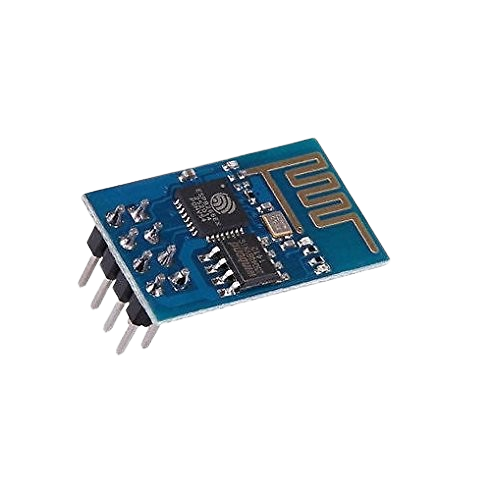
Overview
Introduction
The ESP8266 WiFi module is one of the most popular and affordable chips available for wireless communication and embedded development. It was designed by Espressif Systems and quickly became a favorite choice for students, hobbyists, and professional developers. What makes it so special is that it combines a microcontroller and WiFi capability into a single compact package. This means you can use it not only as a WiFi adapter but also as a complete standalone microcontroller for your electronic projects.
In this guide, we will cover everything about the ESP8266: its features, specifications, pinout details, module types, architecture, applications, and even a practical programming example. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of why this chip has gained such a huge community worldwide.Key Features of ESP8266
The ESP8266 is powerful despite being very small in size. Some of its main features include:-
Supports WiFi standard 802.11 b/g/n
-
Works on 3.0V to 3.6V power supply (3.3V recommended)
-
Low power consumption with deep sleep mode (as low as 10 µA)
-
32-bit Tensilica L106 processor running at 80 MHz (can be overclocked to 160 MHz)
-
Built-in flash memory from 512 KB up to 16 MB depending on the module
-
64 KB instruction RAM and 96 KB data RAM
-
Provides GPIO pins for digital input and output
-
Supports multiple communication protocols such as UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, and PWM
-
Has a 10-bit ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter)
-
Temperature range from -40°C to +125°C
-
Supports WPA and WPA2 security protocols for secure WiFi connections
ESP8266 Pinout and Pin Configuration
The pinout of ESP8266 depends on the module you are using, but some common pins include:-
VCC (3.3V): Power input
-
GND: Ground connection
-
TX/RX: UART serial communication pins
-
CH_PD/EN: Chip enable pin (must be high for the chip to run)
-
RST: Reset pin
-
GPIO pins (0, 2, 15, etc.): Used for digital input/output and special boot functions
-
ADC pin: Reads analog signals up to 1V
When designing a circuit, it is important to note that the ESP8266 is not 5V tolerant. Supplying more than 3.3V can damage the chip.
ESP8266 Variants and Modules
The ESP8266 comes in different module formats and development boards. Here are the most common ones:-
ESP-01:
- One of the earliest versions
- Provides 2 GPIO pins only
- Compact and simple, but limited in functionality
-
ESP-07:
- Comes with an external antenna connector
- Suitable for long-range communication
- Has more GPIO pins compared to ESP-01
-
ESP-12:
- One of the most widely used modules
- Provides many GPIO pins
- Used in popular development boards like NodeMCU
-
NodeMCU Development Board:
- Based on ESP-12 module
- Comes with USB-to-serial converter and voltage regulator
- Beginner-friendly and easy to program using Arduino IDE
-
Wemos D1 Mini:
- Very compact development board
- Compatible with various shields
- Ideal for small projects with limited space
Each variant has its own advantages, but most beginners prefer NodeMCU or Wemos D1 Mini because they are easy to program and provide more flexibility.
Technical Specifications
Here is a summary of the technical specifications of the ESP8266:| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.0V – 3.6V (typical 3.3V) |
| Operating Current | 70 mA – 200 mA |
| Deep Sleep Current | 10 µA |
| Processor | 32-bit Tensilica L106 |
| Clock Speed | 80 MHz (up to 160 MHz) |
| Flash Memory | 512 KB – 16 MB |
| SRAM | 64 KB instruction, 96 KB data |
| GPIO | Up to 17 |
| ADC Resolution | 10-bit |
| WiFi Protocol | IEEE 802.11 b/g/n |
| Security | WPA/WPA2 |
ESP8266 Architecture
The architecture of ESP8266 integrates multiple components into one chip:-
CPU Core (Tensilica L106): Handles processing and program execution
-
RAM and Flash: Stores instructions and data
-
WiFi Transceiver: Manages wireless communication
-
GPIO and Peripherals: Provide input/output control for external devices
-
Power Management: Supports deep sleep and low-power operation
Applications of ESP8266
The ESP8266 is versatile and can be used in many types of electronic systems. Some common applications include:- Wireless data transfer between devices
- Smart controllers for appliances
- Remote monitoring systems
- Home automation systems
- Educational projects and prototyping
- Wireless sensors and control units
- Industrial data logging and control systems
Programming the ESP8266
There are multiple ways to program the ESP8266. The most popular options include:-
Arduino IDE – Easy to use, large community support, beginner-friendly
-
Lua (NodeMCU firmware) – Lightweight scripting language for quick development
-
MicroPython – Lets you program in Python for embedded applications
-
Espressif SDK – Official development kit for advanced programming
Among these, the Arduino IDE is the most commonly used by beginners because it is simple and has plenty of libraries available.
Example Project: Blinking LED with ESP8266
A basic example that demonstrates how to program the ESP8266 is the blinking LED project.Hardware Setup:
- Connect an LED to GPIO2 with a 220Ω resistor
- Connect ground of the LED to GND pin of ESP8266
- Power the ESP8266 using a 3.3V supply
Code (Arduino IDE):
This simple program turns the LED on and off every second. It is a beginner-friendly example to understand how the GPIO pins work.
Advantages of ESP8266
- Very low cost compared to other wireless modules
- Small in size but powerful in performance
- Built-in WiFi with strong connectivity
- Wide support from the developer community
- Multiple programming options available
- Low power modes for energy-efficient systems
Limitations of ESP8266
- Works only on the 2.4 GHz WiFi band (no 5 GHz support)
- Limited GPIO pins compared to larger microcontrollers
- Requires 3.3V regulated power supply (not 5V tolerant)
- Single-core processor, less powerful than newer modules like ESP32
Conclusion
The ESP8266 WiFi module is an excellent choice for anyone looking to add wireless capability to electronic systems. It combines a microcontroller and WiFi in a compact, affordable package, making it perfect for both beginners and advanced developers. With different module types, flexible programming support, and strong community resources, it continues to be one of the most widely used chips in embedded electronics.
Whether you are learning the basics with a simple LED blinking project or developing complex wireless applications, the ESP8266 gives you the tools to build reliable, efficient, and cost-effective systems.
Where to Buy
Prices may vary. Click on "Buy Now" to check current availability and pricing.
Administrator
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about ESP8266 WiFi Module: Features, Specifications, Pinout, and Programming Guide. Find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
User Reviews & Comments
Share your experience with this IoT Blog. Your feedback helps our community make informed decisions!
Share Your Experience
Help others by sharing your thoughts about this IoT Blog.
Related Blogs
Explore more IoT Blogs in the same category
Arduino Uno: A Complete Guide for Beginners and IoT Enthusiasts (2025 Edition)
Microcontroller
Arduino Uno is a beginner-friendly microcontroller board based on ATmega328P, ideal for IoT and electronics projects. This guide covers its features, specifications, and practical applications to help you build smart systems easily and efficiently.
What is ESP32 in IoT?
Microcontroller
Discover the complete guide to ESP32 with detailed pinout, specifications, and project ideas. Learn how to use ESP32 for embedded systems, automation, smart devices, and real-time applications. Ideal for developers, engineers, and students looking for fast and efficient IoT development. Unlock the power of ESP32 in your next smart project.
What is ESP8266? Architecture, Pinout, Programming aur Applications
Microcontroller
This guide covers proven strategies to create technical content that drives traffic, increases visibility. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned blogger, learn how to write about ESP8266, keyword placement, and reader engagement — without compromising content quality.
No Reviews Yet
Be the first to share your experience with this IoT Blog!