Rain Sensor in IoT: Working, Applications, and Benefits Explained
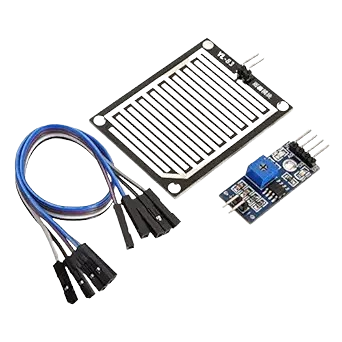
Overview
Introduction
Technology has changed the way we live, and one such small but powerful invention is the rain sensor. A rain sensor is a device that can detect rainfall and send a signal to control different systems automatically. From turning on car wipers during rain to stopping irrigation in farms, this device plays a big role in making life easier and smarter. The importance of rain sensors has increased over the years because of their ability to save resources like water and energy, while also providing comfort and safety. In this article, we will explore everything about rain sensors, including how they work, their types, applications, benefits, and even a real-life example.What is a Rain Sensor?
A rain sensor is an electronic device that senses the presence or amount of rain. Once it detects water droplets, it sends an electrical signal to other systems to perform a certain action. For example, in agriculture, if it starts raining, the sensor can automatically stop the irrigation system to avoid wasting water. In cars, the sensor can turn on the windshield wipers without the driver’s effort. In short, it is a smart device that connects with other machines or systems to make decisions automatically whenever rainfall occurs.How Does a Rain Sensor Work?
The working principle of a rain sensor depends on the technology it uses. However, the basic process is quite simple and involves three steps:-
Detection of Rain – The sensor detects raindrops either by using light refraction (in optical sensors) or by sensing the conductivity of water on its surface.
-
Signal Processing – Once rain is detected, the sensor converts this information into an electrical signal.
-
Action Trigger – The signal is then sent to a connected system, such as an irrigation pump, car wiper, or smart home device, to take the required action.
Main Components of a Rain Sensor
-
Sensing Surface – The part of the sensor that comes in contact with raindrops.
-
Electronic Circuit – Processes the rain detection and generates signals.
-
Output Module – Sends signals to other systems like pumps or motors.
-
Protective Case – Covers the sensor to make it weatherproof and durable.
Types of Rain Sensors
-
Optical Rain Sensor
- Uses light refraction to detect raindrops.
- Mostly used in cars for automatic windshield wipers.
- Can also measure rainfall intensity.
-
Conductive Rain Sensor
- Uses a conductive plate with tracks.
- When raindrops fall, they connect the tracks and allow current to flow.
- Mostly used in irrigation systems and garden devices.
-
Capacitive Rain Sensor
- Works by detecting changes in capacitance when water collects on the surface.
- More accurate in detecting light rain.
-
Resistive Rain Sensor
- Detects change in resistance when water connects two points.
- Simple and affordable option.
Applications of Rain Sensors
- Automobiles
Rain sensors are commonly installed in cars. When it starts raining, the sensor automatically switches on the windshield wipers. It can also control the speed of wipers depending on the amount of rain, which improves safety for the driver and passengers. - Agriculture
In farming, rain sensors are connected with irrigation systems. When rainfall is detected, the irrigation stops automatically. This saves water, prevents overwatering of crops, and ensures better farm management. - Home Automation
Rain sensors are used in smart homes for automatic window closing, roof covers, and garden watering systems. For example, if it starts raining, windows can close automatically to prevent damage inside the house. - Weather Monitoring Stations
Rain sensors are installed in weather stations to measure rainfall. This data helps in weather forecasting and environmental studies. - Industrial Applications
Industries use rain sensors to protect machinery placed outdoors. When rain is detected, machines can be covered or stopped to prevent damage.
Advantages of Rain Sensors
-
Saves Water – Prevents unnecessary irrigation.
-
Convenient – Provides automatic operation without human effort.
-
Safe Driving – In cars, improves driver safety by starting wipers on time.
-
Energy Efficient – Reduces power usage by switching off devices when not needed.
-
Durable – Designed to work in outdoor conditions.
-
Cost-Effective – Long-term savings on water and maintenance.
Limitations of Rain Sensors
- Needs proper calibration for best results.
- Dust or dirt on the sensor can reduce accuracy.
- Initial cost of installation can be high in some systems.
- Some sensors may not detect very light rain accurately.
Real-Life Example of a Rain Sensor
A popular example is in modern cars. An optical rain sensor is placed near the rearview mirror. When raindrops fall on the windshield, the sensor detects them instantly. The system then sends a signal to the wipers, which start moving automatically. If the rain becomes heavier, the speed of the wipers increases without the driver doing anything. This makes driving safer and more comfortable, especially during sudden showers.
Future Scope of Rain Sensors
With the rise of smart technology and environmental concerns, rain sensors are expected to become even more advanced. Future sensors may provide more accurate rainfall measurements, connect wirelessly to smart devices, and play a bigger role in sustainable farming and smart cities. As automation grows, rain sensors will continue to be a key part of everyday life.Conclusion
Rain sensors may look small, but they play a very big role in modern life. Whether it is saving water in farms, providing safety in cars, or helping with home automation, these devices are extremely useful. They make systems smarter, more efficient, and environment-friendly. As technology continues to improve, rain sensors will become even more common and important in the future.Where to Buy
Prices may vary. Click on "Buy Now" to check current availability and pricing.
Administrator
Frequently Asked Questions
Common questions about Rain Sensor in IoT: Working, Applications, and Benefits Explained. Find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
User Reviews & Comments
Share your experience with this IoT Blog. Your feedback helps our community make informed decisions!
Share Your Experience
Help others by sharing your thoughts about this IoT Blog.
Related Blogs
Explore more IoT Blogs in the same category

Joystick Module for IoT: Types, Working, Pinout, Interfacing, and Applications Explained
Input Devices
Learn everything about Joystick Module for IoT projects including its types, working principle, pinout diagram, Arduino interfacing, and real-life applications. This guide is perfect for electronics hobbyists and students building smart control systems using joystick sensors.

Push Button in IoT: Working, Applications & Wiring Explained
Input Devices
Learn everything about Push Buttons in IoT devices, including their working, wiring techniques, and real-time applications. This detailed guide helps electronics beginners and developers understand how push buttons are used in smart systems. Perfect for IoT-based projects and educational use. Discover how this small component plays a big role in modern automation.
Potentiometer: Types, Working Principle, Applications, Advantages & Selection Guide
Input Devices
A potentiometer is a three-terminal variable resistor used to control voltage and current in electronic circuits. This detailed guide explains potentiometer types, working principle, applications, and benefits, along with tips for choosing the right one. Perfect for students, hobbyists, and professionals seeking clear, accurate, and practical information.
No Reviews Yet
Be the first to share your experience with this IoT Blog!